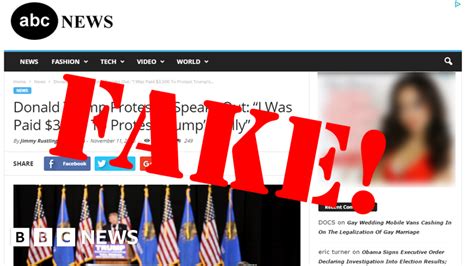
Decode Misleading News: A Guide to Spotting Truth Misleading news is everywhere these days, flooding our feeds and conversations. Guys, it’s not just a buzzword; it’s a serious challenge that affects how we understand the world, make decisions, and even impacts our relationships. From political campaigns to public health crises,
misleading news
has shown its power to sway opinions, spread panic, and erode trust in legitimate institutions. Think about it: every day, we’re bombarded with countless pieces of information – articles, social media posts, videos, podcasts – and it’s getting harder than ever to distinguish between what’s real and what’s, well, total bunk. This isn’t just about sensational headlines; it’s about cleverly disguised falsehoods that look and feel like credible reporting. The sheer volume makes it tough, but the
sophistication of misleading news
is what truly makes it a formidable opponent in the battle for truth. We’ve seen how stories designed to mislead can go viral in minutes, reaching millions before anyone has a chance to fact-check them. This rapid dissemination means that by the time corrections are issued, the
damage caused by misleading news
has often already been done, leaving a lasting impression on public perception. It influences everything from how we vote to what vaccines we trust, or even what products we buy. The digital age has amplified this problem tenfold, giving anyone with an internet connection the ability to publish and distribute content globally, without the traditional gatekeepers of journalism. This democratic access is a double-edged sword: while it empowers diverse voices, it also opens the floodgates for those with less-than-honorable intentions to spread
misleading news
and
disinformation
. Our collective ability to navigate this complex information landscape is crucial for a healthy democracy and an informed society. Without a solid understanding of how to identify and
decode misleading news
, we risk being manipulated, making poor choices, and contributing to a cycle of misinformation that harms us all. This guide, folks, is designed to equip you with the essential tools and knowledge to become a savvy consumer of news, empowering you to
spot misleading news
and champion the truth in your daily life. It’s about being
proactive in your information consumption
, rather than passively absorbing whatever pops up on your screen. So, let’s dive in and learn how to navigate this wild world of information, shall we? ## Understanding What Misleading News Really Is To truly
decode misleading news
, we first need to get a grip on what we’re actually talking about. The term “misleading news” is often thrown around casually, but it actually encompasses a spectrum of intentionality and accuracy. It’s not always as simple as “true or false.” Sometimes, it’s a mix of facts twisted to fit a narrative, or information presented out of context.
Understanding the nuances of misleading news
is key to effectively identifying it. It’s more than just a typo or an innocent mistake;
misleading news
often has a deliberate purpose behind it, whether to provoke a reaction, sow division, or simply generate clicks and revenue. This section will break down the different flavors of
misleading news
and explore the psychological reasons why we sometimes fall for it, even when we think we’re being careful. We’ll differentiate between outright fabrication and more subtle forms of manipulation, helping you build a more robust framework for evaluating the information you encounter. This foundational knowledge is paramount for anyone serious about becoming a
master at spotting misleading news
. ### Fake News vs. Misinformation vs. Disinformation: What’s the Difference? Alright, guys, let’s clear up some common confusion around terms like
fake news
,
misinformation
, and
disinformation
. While often used interchangeably, these terms have distinct meanings, and understanding them is crucial for anyone trying to
decode misleading news
. First up,
fake news
is probably the term you hear most often. In its purest sense,
fake news
refers to completely fabricated content designed to deceive, often presented as legitimate journalistic reporting. Think entirely made-up stories, non-existent quotes, or photoshopped images presented as real. These pieces are created with the express intention to mislead and can range from outlandish hoaxes to sophisticated propaganda. They are designed to mimic real news outlets, making it harder for an unsuspecting reader to immediately tell the difference. The goal is typically to influence public opinion, generate viral shares, or even just to earn advertising revenue from clicks. It’s the most extreme end of the
misleading news
spectrum, where there’s no factual basis whatsoever. Next, we have
misinformation
. This term refers to
false or inaccurate information
that is
unintentionally
spread. The key here is the lack of malicious intent. Someone sharing misinformation genuinely believes it to be true, or doesn’t realize it’s false, and passes it along without intending to deceive. For example, a friend might share an outdated article about a health remedy thinking it’s helpful, not knowing the information has since been debunked. Or someone might misinterpret a scientific study and post about it, leading others to believe something incorrect. While the intent isn’t malicious, the
spread of misinformation
can still have very real and harmful consequences, especially in areas like public health or safety. It often arises from genuine errors, misunderstandings, or simply not having access to the full context.
Spotting misinformation
requires a keen eye for detail and a willingness to verify, even when the source seems trustworthy. Finally, there’s
disinformation
. This is where things get really
spicy
and often more dangerous.
Disinformation
is
false information that is deliberately and intentionally created and disseminated
to deceive, manipulate, or cause harm. Unlike misinformation, the people behind disinformation know it’s false and actively work to spread it for a specific agenda. This agenda could be political (e.g., influencing elections, discrediting opponents), financial (e.g., manipulating stock prices, promoting scams), or social (e.g., sowing discord, inciting hatred).
Disinformation campaigns
are often highly organized, well-funded, and can involve sophisticated tactics like bot networks, deepfakes, and coordinated amplification across social media platforms. It’s the weaponization of information, and it’s a primary concern when we talk about
combating misleading news
. Recognizing disinformation means looking beyond the surface and asking: “Who created this, and why?” It’s a deliberate act of deception designed to control narratives and perceptions. Being able to distinguish between these three categories is your first big step in becoming a
master investigator of misleading news
, helping you not only identify false content but also understand the motivations behind its creation and spread. This understanding empowers you to respond appropriately, whether it’s simply correcting a friend or reporting a malicious campaign. ### The Psychology Behind Believing Misleading News So, why do we sometimes fall for
misleading news
, even when the red flags seem obvious in hindsight? It’s not always about a lack of intelligence, guys; it’s often about our inherent psychological biases.
Understanding the psychology behind believing misleading news
is a critical component of learning to
spot misleading news
effectively. One of the biggest culprits is
confirmation bias
, a fancy term for our tendency to seek out, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms our pre-existing beliefs or hypotheses. If a piece of
misleading news
aligns with what we already think or
want
to believe, we’re far more likely to accept it as true without critical scrutiny. It feels good to have our beliefs validated, even by false information, and our brains often prefer that comfort over the discomfort of confronting conflicting facts. Then there’s the
bandwagon effect
, which plays a huge role in the
spread of misleading news
. We’re social creatures, and if we see many people in our social circle, or even just online, sharing or believing something, we’re more prone to believe it too. The perception of popularity can be a powerful, albeit often inaccurate, indicator of truth. This is particularly potent on social media, where algorithms often show us what our connections are interacting with, creating echo chambers and filter bubbles that reinforce our existing views and make
misleading news
seem more prevalent and credible than it might actually be. Another factor is
emotional reasoning
.
Misleading news
often taps directly into our emotions – fear, anger, outrage, joy, or even hope. When content evokes a strong emotional response, our logical, critical thinking skills can take a backseat. We’re more likely to share something that makes us feel strongly, without pausing to verify its accuracy. This is why sensational headlines and emotionally charged stories are so effective in spreading
misleading news
; they bypass our rational filters. The
illusion of truth effect
also contributes significantly. This psychological phenomenon describes how repeated exposure to a statement increases its perceived truthfulness. The more often we hear or see a piece of
misleading news
, even if we initially dismiss it, the more likely we are to start believing it, simply because of its familiarity. This is a powerful tool for
disinformation campaigns
, which often rely on relentless repetition to embed false narratives in the public consciousness. Finally, our
cognitive load
in the modern information environment is immense. We’re constantly processing so much data that our brains look for shortcuts. We might rely on heuristics (mental shortcuts) like judging credibility based on how professional a website looks, or who shared it, rather than digging into the actual facts. When we’re tired, stressed, or just overwhelmed, our ability to critically evaluate information diminishes, making us more susceptible to
misleading news
. Being aware of these psychological vulnerabilities isn’t about blaming ourselves, but about recognizing the battleground and arming ourselves with strategies to overcome these natural human tendencies when confronted with
misleading news
. It’s about being
mindful and deliberate
in our information consumption. ## Practical Tips for Spotting Misleading News Like a Pro Now that we understand the landscape of
misleading news
and why it works, it’s time to get practical, folks. Learning to
spot misleading news
effectively isn’t rocket science, but it does require a bit of effort and a systematic approach. Think of yourself as a detective, always looking for clues and inconsistencies. These tips will arm you with the essential techniques to
decode misleading news
and become a more discerning consumer of information. It’s about developing a healthy skepticism, not cynicism, and asking the right questions before accepting anything at face value. With practice, these actions will become second nature, transforming you into a powerful
advocate for truth
in your own digital space. We’re going to break down several actionable strategies that you can apply to every piece of news you encounter, from a quick social media post to an in-depth article. ### Check the Source: Go Beyond the Headline, Guys! The absolute first step in learning to
spot misleading news
is to
check the source
– and I mean
really
check it, beyond just the headline. Don’t just read the juicy title and share; take a moment, a deep breath, and click through. Who published this? Is it a recognized, reputable news organization known for journalistic integrity, or is it a website you’ve never heard of before? A quick way to do this is called “lateral reading.” Instead of staying on the questionable site and looking for clues
within
it, open a new tab and search for information
about
the source itself. For instance, if you see an article from “Daily Global Truths,” Google “Daily Global Truths bias” or “Daily Global Truths reputation.” You might quickly discover it’s a known propaganda site, a satirical outlet, or a blog run by someone with a clear agenda, not a journalistic organization. Look at the website’s URL. Does it seem legitimate, or is it trying to impersonate a well-known news site with a slightly altered domain name (e.g., “cn-news.com” instead of “cnn.com”)? These subtle changes are often indicators of
misleading news
. Also, investigate the “About Us” page. A credible news source will have a transparent “About Us” section, detailing its mission, editorial standards, funding, and the names of its leadership and journalists. If this information is missing, vague, or filled with hyperbolic claims about being the “only source of real truth,” that’s a huge red flag that you’re likely dealing with
misleading news
. Be wary of sites that solely publish opinion pieces presented as news, or those that heavily rely on anonymous sources without any justification. Consider the overall look and feel of the website. While not foolproof, many
misleading news
sites might have unprofessional layouts, an excessive amount of aggressive pop-up ads, or grammatical errors that a professional newsroom would quickly catch. These aren’t definitive proof of
misleading news
, but they are often accompanying symptoms. Furthermore, evaluate the age of the website and its content. Is it a brand new site that popped up overnight? Does it have a very short history of publishing, or does it primarily publish highly partisan or inflammatory content? Legitimate news organizations typically have a long history, clear editorial policies, and a diverse range of reporting. Developing this habit of
source verification
is one of the most powerful tools in your arsenal against
misleading news
. It’s like checking the label on food before you eat it; you want to know what you’re consuming and who made it. Don’t be lazy, guys – your informed mind depends on it! This proactive approach helps to
decode misleading news
right at the initial point of contact. ### Scrutinize the Content: Look for Red Flags Once you’ve checked the source, your next move in learning to
spot misleading news
is to
scrutinize the content
itself. This means reading the article, or watching the video, with a critical eye, actively looking for warning signs. The content of
misleading news
often gives itself away through specific characteristics. Firstly, pay close attention to the
headline
. Is it sensational, overly emotional, or using all caps and excessive exclamation marks?
Misleading news
headlines are often designed to shock, outrage, or provoke an immediate emotional response, compelling you to click and share without thinking. Legitimate news usually has a more neutral, informative headline that accurately reflects the article’s content. If the headline seems too wild to be true, it probably is
misleading news
. Next, examine the
language and tone
used in the body of the text. Is it highly opinionated, biased, or using loaded words? Does it express strong emotional language rather than presenting facts objectively? Reputable journalism aims for neutrality and presents different sides of a story where appropriate.
Misleading news
, on the other hand, often employs emotionally manipulative language, personal attacks, or straw man arguments to discredit opposing viewpoints without presenting factual counter-arguments. Look for generalizations, sweeping statements, and a lack of nuance. Be on the lookout for
grammatical errors and typos
. While even professional outlets make mistakes, a high frequency of errors can be a sign that the content hasn’t gone through a rigorous editorial process, which is common in
misleading news
operations. Similarly, check for
unusual formatting or design choices
. If the text suddenly changes font, has odd spacing, or looks generally amateurish, it might indicate a less-than-professional source. Also, consider the
date of publication
. Sometimes,
misleading news
isn’t entirely false, but it’s old news presented as current. An event from five years ago might be republished to create a false sense of urgency or relevance to a current situation. Always check the date to ensure the information is fresh and pertinent. Finally, and this is a big one, watch out for
exaggeration or omission
.
Misleading news
often takes a kernel of truth and blows it out of proportion, or it cherry-picks facts while deliberately leaving out crucial context that would change the entire narrative. It’s not always about outright lies; sometimes it’s about presenting a skewed version of reality.
Decoding misleading news
effectively requires you to be alert to these subtle distortions, ensuring you’re getting the full, unvarnished picture, not just the bits and pieces that support a specific agenda. This careful internal scrutiny helps you confirm or deny your initial suspicions about the source and its intent. ### Verify Supporting Evidence: Trust, But Verify! Alright, truth-seekers, after you’ve scrutinized the source and the content, your next critical step in learning to
spot misleading news
is to
verify the supporting evidence
. This is where the detective work really gets fun! A credible news story will always back up its claims with evidence: quotes from named experts, links to original research, statistics from authoritative bodies, or references to official documents.
Misleading news
often either lacks such evidence entirely or presents it in a way that’s difficult to verify. If statistics are cited, ask yourself:
Where do these numbers come from?
Is there a link to the original study or data source? If the article says, “Studies show…”, but doesn’t name the studies or provide links, that’s a huge red flag. Good journalism will always attribute its data. Don’t just take their word for it; actually click on those links! Do they lead to the original source, or to another opinion piece, or even a broken page? If the source cited is an obscure blog or an advocacy group with a clear agenda, treat it with extreme caution. Genuine academic studies or government reports will typically come from universities, research institutions, or official government websites.
Verifying evidence
is about tracing the information back to its origin. Pay attention to
quotes
. Are people quoted by name, with their affiliations listed? Are there “anonymous sources” without any explanation of why their anonymity is necessary? While anonymous sources are sometimes used in investigative journalism to protect whistleblowers, their use should be rare and clearly justified by the publication.
Misleading news
often fabricates quotes or attributes them to vague entities like “sources close to the matter” or “many believe.” If an image or video is used, consider its origin. Tools like Google Reverse Image Search can help you determine if an image has been used out of context, doctored, or is much older than the story implies. Many
misleading news
stories rely on old images to illustrate current events, giving a false impression of what’s happening. Another crucial aspect of
verifying supporting evidence
is to
cross-reference
. Once you’ve identified the core claims, open a few other tabs and see how other reputable news outlets are reporting on the same event or topic. If only one obscure website is reporting something extraordinary, and no major news organizations have picked it up, that’s a strong indicator you might be dealing with
misleading news
. Conversely, if multiple independent, credible sources are reporting the same facts, that significantly increases the likelihood of accuracy. This isn’t about finding outlets that agree with your viewpoint, but about finding multiple
independent verifications
of the same core facts. This diligent approach to
evidence verification
is fundamental to your ability to
decode misleading news
and ensure that the information you consume is built on a solid foundation of truth. Don’t be afraid to put in the legwork, folks; your critical thinking muscles will thank you! ### Consider the Intent: Who Benefits from This Story? This next tip for
spotting misleading news
dives a little deeper, moving beyond the obvious to ask a crucial question:
Who benefits from this story?
Understanding the potential intent behind a piece of content can be incredibly illuminating in your quest to
decode misleading news
. Every piece of information, especially online, exists for a reason. Sometimes it’s simply to inform, but often there’s an underlying agenda, even if it’s just to get clicks for advertising revenue.
Political Agendas
: Many
misleading news
stories are designed to influence political discourse, sway elections, or disparage political opponents. If an article strongly favors one political party or ideology, or demonizes another, consider its motivations. Is it trying to rally support, sow division, or simply spread propaganda? These stories are often heavily biased, presenting only one side of an issue or exaggerating facts to fit a political narrative. Recognizing this intent helps you approach the content with the necessary skepticism.
Financial Motivations
: Don’t underestimate the power of money. Some
misleading news
is created purely for financial gain. Sensational or outrageous headlines generate clicks, and clicks generate advertising revenue. Fake news websites often profit from programmatic advertising, where advertisers unknowingly place ads on these sites. Other times, the intent might be to manipulate markets, promote certain products (sometimes disguised as reviews), or drive traffic to scam websites. If a story seems too good to be true, or suspiciously pushes a particular product or service, dig deeper into the potential financial incentives of its creators.
Social or Ideological Agendas
: Beyond politics and money,
misleading news
can also be driven by social or ideological motivations. This could involve promoting specific social movements, spreading conspiracy theories, or pushing certain moral or ethical viewpoints. These stories often appeal to strong emotions and aim to reinforce group identity or spark collective action. While advocating for a cause isn’t inherently bad,
misleading news
used in this context often distorts facts or invents narratives to achieve its goals, rather than relying on truth and evidence.
Personal Brand or Influence
: In the age of social media influencers, some individuals might create or share
misleading news
to boost their own profile, gain followers, or establish themselves as authorities on a topic, even if their “authority” is built on shaky ground. The desire for viral fame or personal influence can be a powerful motivator for spreading
misleading news
. By asking “Who stands to gain?” or “What purpose does this serve?”, you’re moving beyond just the accuracy of the facts and delving into the deeper context of
why
this information exists. This critical inquiry empowers you to
decode misleading news
by identifying the underlying forces and intentions that often shape its creation and dissemination. It’s a crucial step for truly understanding the digital information ecosystem, folks. ### Leverage Fact-Checking Tools and Resources When all else fails, or when you simply want a quick, authoritative check, leveraging
fact-checking tools and resources
is an indispensable part of learning to
spot misleading news
. You don’t have to be a lone wolf in this battle, guys; there’s a whole army of dedicated fact-checkers out there doing the heavy lifting! These organizations are specifically designed to investigate claims, debunk falsehoods, and provide verified information. One of the best ways to use these resources is to search for the specific claim you’re investigating on their websites. Major
fact-checking organizations
like
Snopes
,
PolitiFact
,
FactCheck.org
, and
AFP Fact Check
are goldmines of verified information. They thoroughly research viral claims, political statements, and popular internet myths, providing detailed analyses and conclusions about their accuracy. Before you share that outrageous story about aliens building pyramids, a quick search on one of these sites could save you from spreading
misleading news
. Many of these sites also explain
how
they reached their conclusions, often linking to original sources and expert opinions, which can further educate you on critical thinking and
evidence verification
. This transparency is key to their credibility. Beyond general fact-checking sites, there are also specialized resources. For medical claims, consult reputable health organizations like the
World Health Organization (WHO)
or the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
. For scientific claims, look for consensus from established scientific bodies or peer-reviewed journals. Furthermore, consider using browser extensions that provide
fact-checking information
directly in your feed. While not all are perfect, some can give you immediate context about a source’s bias or reputation. However, always exercise caution and verify the extension’s credibility before relying on it too heavily. Think of these tools as your critical thinking sidekicks. They’re there to help you
decode misleading news
faster and more reliably, especially when you’re short on time or dealing with a complex issue. Remember, the goal isn’t just to be told what’s true or false, but to understand
why
it’s true or false. These
fact-checking resources
provide not just answers, but also valuable insights into the
mechanisms of misleading news
and how to dismantle it. Integrating these tools into your regular news consumption habits will significantly boost your ability to
spot misleading news
and contribute to a more informed digital environment for everyone. It’s about empowering yourself with knowledge and knowing where to turn when you need an expert opinion on the veracity of a claim. ## The Impact of Misleading News and Our Role in Combating It Guys, the consequences of
misleading news
aren’t just theoretical; they have very real, tangible impacts on individuals, communities, and global society.
Understanding the profound impact of misleading news
is crucial for appreciating why our collective efforts to
combat misleading news
are so vital. When false information spreads, it erodes trust – trust in institutions, trust in journalism, and even trust in each other. This erosion of trust can destabilize democracies, polarize societies, and make it incredibly difficult to address shared challenges, from climate change to public health. On a personal level, believing
misleading news
can lead to poor decision-making. Imagine making health choices based on false remedies, or financial investments based on fabricated market data. The repercussions can be devastating. Moreover, the constant exposure to
misleading news
, particularly emotionally charged disinformation, can contribute to anxiety, stress, and a general sense of overwhelm or helplessness about the state of the world. It creates a confusing information environment where it’s hard to discern reality. Beyond personal harm,
misleading news
often fuels division and hatred. It’s frequently used to dehumanize minority groups, spread xenophobia, or incite violence. We’ve seen countless examples where
disinformation campaigns
have exacerbated social tensions, leading to real-world clashes and persecution. It can also undermine scientific consensus, leading to skepticism about established facts and hindering progress on critical issues. Think about the challenges in vaccine uptake or climate action when
misleading news
sows doubt among the public. So, what’s
our role in combating misleading news
? It’s huge, folks! Every single one of us has a responsibility in this digital ecosystem. First and foremost, apply the tips we just discussed:
check the source, scrutinize the content, verify evidence, and consider the intent
. Be a responsible consumer of information. Don’t be a passive recipient; be an active investigator. Secondly,
think before you share
. Before hitting that retweet or share button, ask yourself: “Is this accurate? Is this helpful? Am I contributing to the spread of
misleading news
?” A moment of critical reflection can prevent a false story from going viral. Thirdly,
educate others
respectfully. If you see a friend or family member sharing
misleading news
, gently point them towards reliable sources or fact-checks. It’s not about shaming, but about fostering a more informed community. We can also support reputable journalism and
fact-checking organizations
through subscriptions or donations, recognizing the essential work they do in the face of
misleading news
. Finally, advocate for platforms to take greater responsibility in moderating and curbing the
spread of misleading news
. Our collective vigilance and action are our strongest defenses against the insidious nature of
misleading news
. It’s a continuous battle, but by working together and staying informed, we can build a more resilient and truthful information environment. This is not just about protecting ourselves, but about protecting the integrity of our society. ## Empowering Yourself in the Digital Age: Your Guide to Truth We’ve covered a lot of ground, guys, and hopefully, you’re feeling more confident and empowered in your ability to
decode misleading news
. In this fast-paced digital age, where information, both good and bad, flies at us from every direction, being able to
spot misleading news
isn’t just a nice skill to have; it’s an essential survival tool. Think of this guide as your personal roadmap to navigating the often-treacherous waters of online information. You now have a robust toolkit, equipped with strategies to critically evaluate sources, dissect content, verify evidence, understand underlying motives, and utilize expert fact-checking resources. Remember, the journey to becoming a truly discerning news consumer is ongoing. The tactics used to spread
misleading news
are constantly evolving, so our vigilance must also evolve. Stay curious, stay skeptical (in a healthy way!), and always be willing to learn and adapt. Regularly practicing these critical thinking habits will strengthen your “misleading news detector” and make you less susceptible to manipulation. It’s about building a muscle, folks, and the more you use it, the stronger it gets. Don’t be discouraged if you occasionally encounter a piece of
misleading news
that initially fools you; even the pros get caught out sometimes. The key is to learn from those instances and refine your approach. Beyond protecting yourself, your newfound skills have a broader impact. By refusing to spread
misleading news
and by sharing accurate information, you become a force for good in the digital world. You contribute to a more informed public discourse, helping to elevate truth and reason over sensationalism and falsehoods. You become a crucial part of the solution to one of the biggest challenges facing our modern society. So go forth, be the truth-seeker, the myth-buster, the informed citizen! Your commitment to truth empowers not just yourself, but everyone around you. Let’s make the internet a smarter, more reliable place, one verified story at a time. You’ve got this, and together, we can truly
decode misleading news
and champion a future built on facts.

